Mazes for behavioral testing
We offer a wide range of mazes and open fields for your standard tests. Check this overview of some of the mazes we provide. Are you looking for a different maze? Then, contact us to see how we can help you.
- Perfectly suited for video tracking with EthoVision XT
- Any type of maze for any size animal
- Click the links to learn more about how to use the mazes
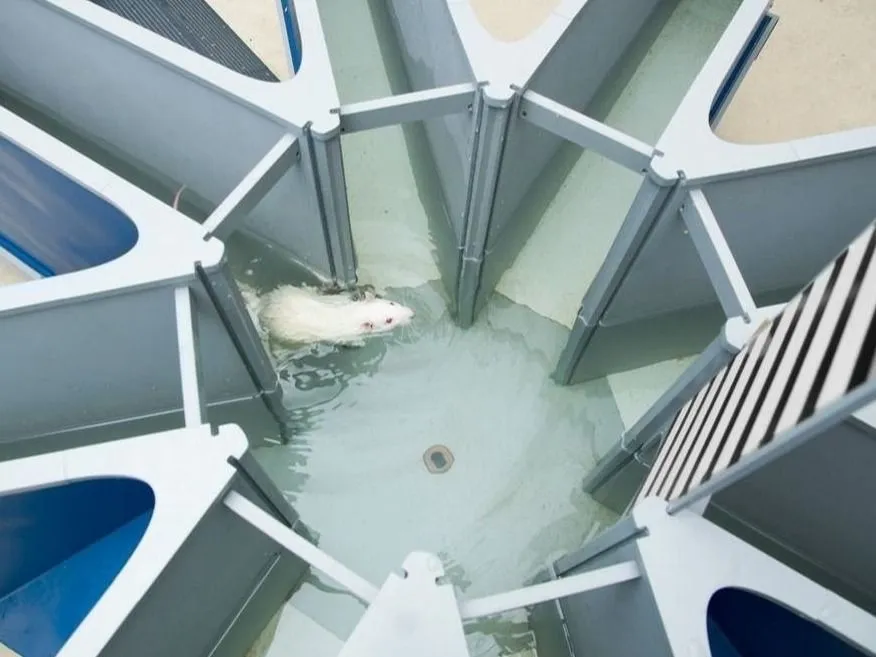

Mazes and open fields
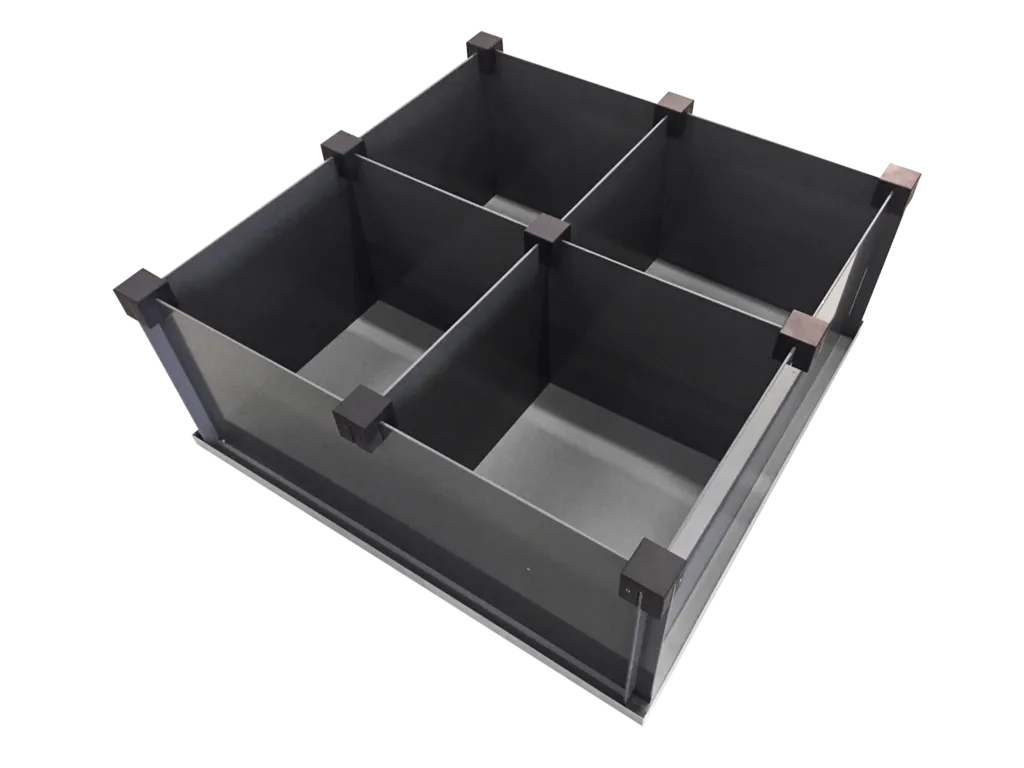

Open field
The open field test is a straight-forward test to investigate activity, anxiety-related and exploratory behavior of rodents. It features one or more square arenas.
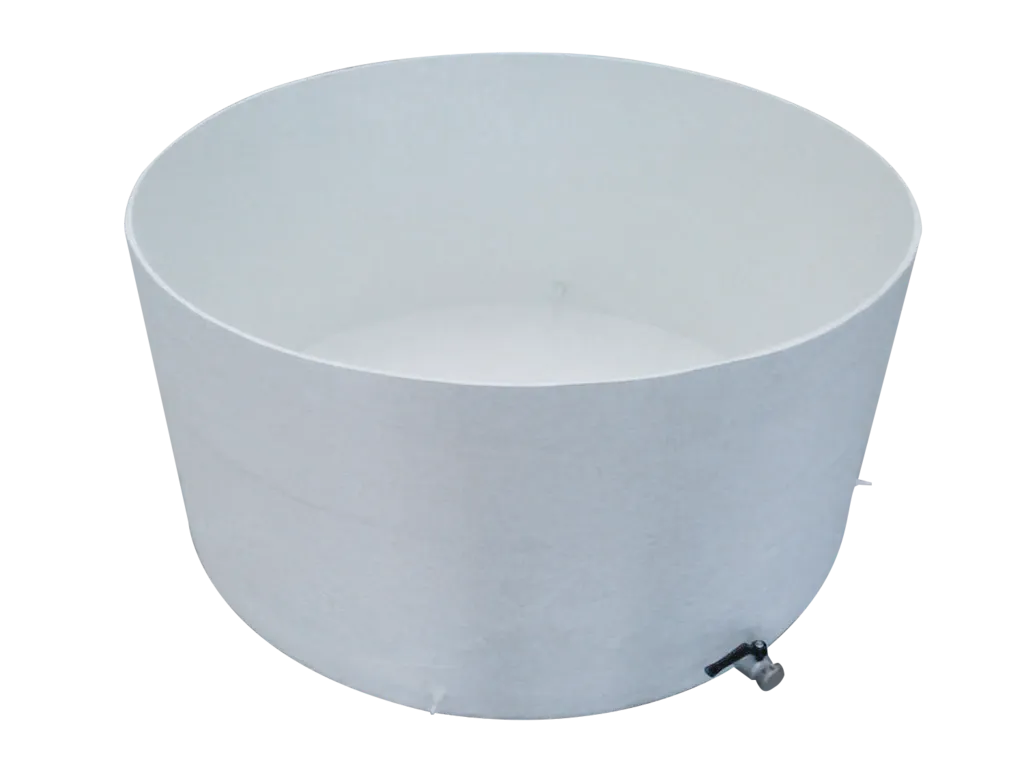

Morris water maze
The Morris water maze task is a popular and well-validated test for spatial learning: most-used behavioral test in neuroscience research.
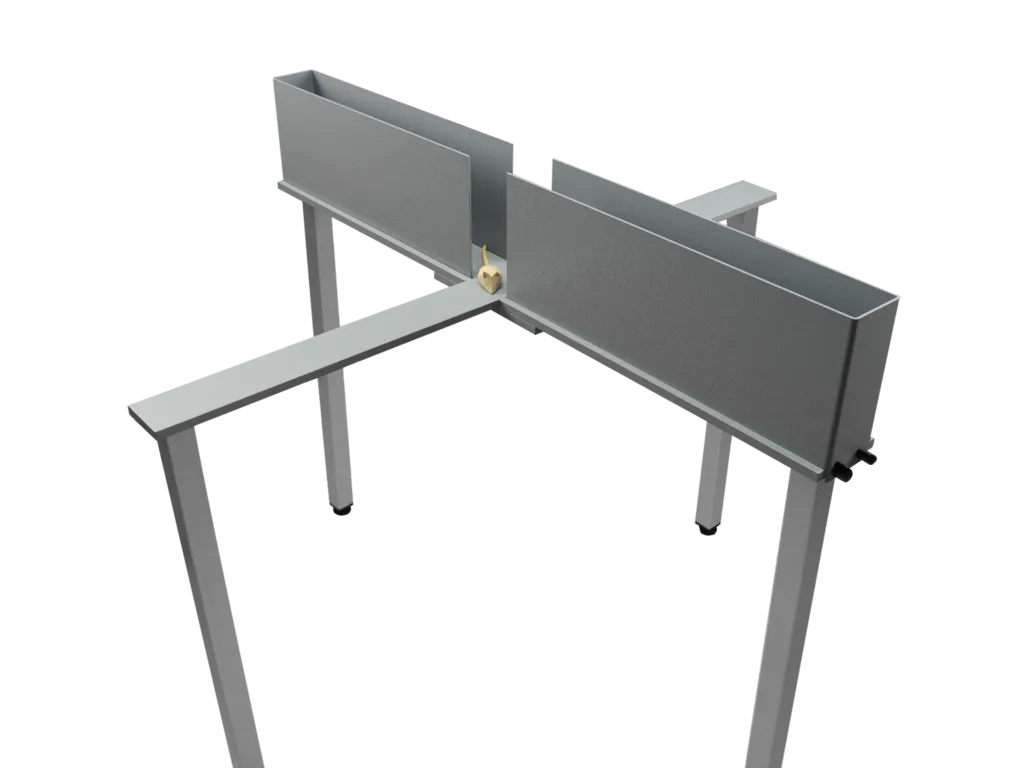

Elevated plus maze
The EPM is a well-characterized behavioral paradigm, one of the most used tests for anxiety research. Anxious animals will spend more time in the closed arms.
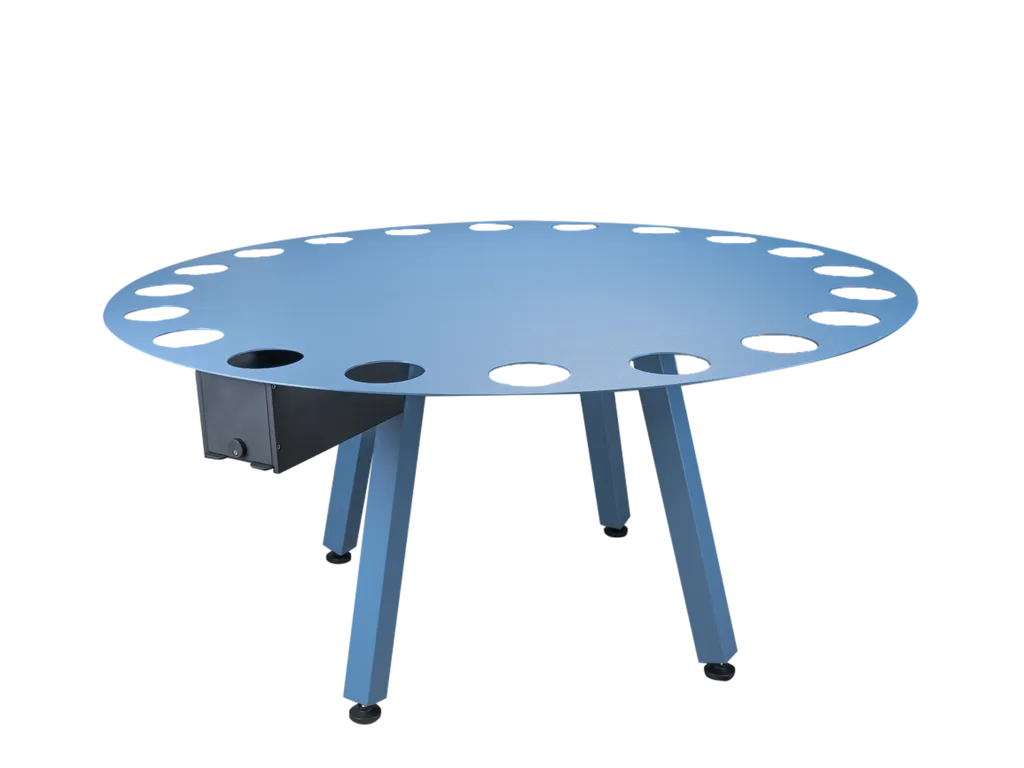
Barnes maze
The Barnes maze is a paradigm to study spatial learning and memory. It consists of a circular table with holes around the circumference.
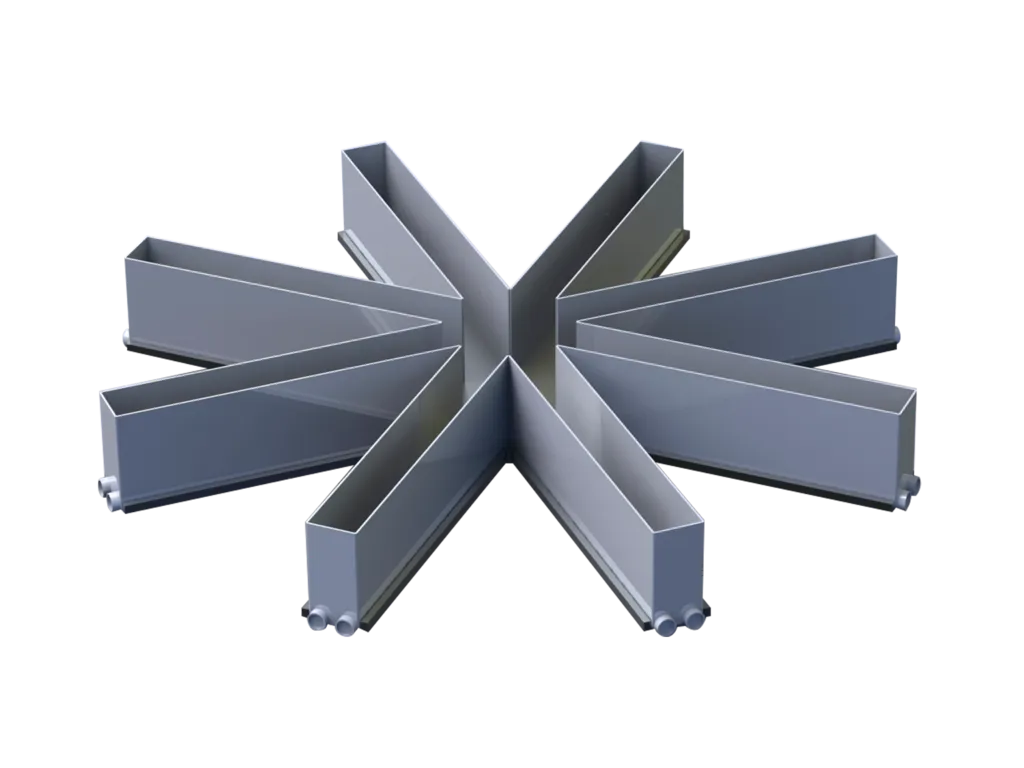

Radial arm maze
The radial arm maze is test for spatial / working / reference learning and memory in rats and mice, for several sophisticated test protocols.
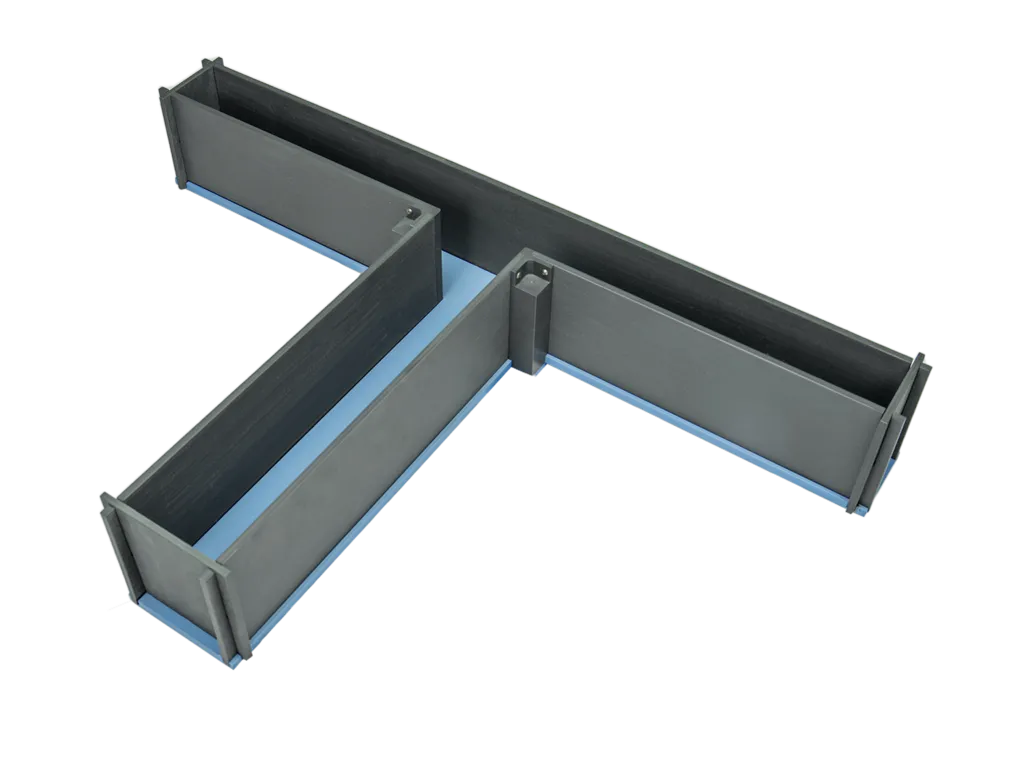
T-maze
The T-maze task is an investigation of spatial learning and memory. Subsequently, reversal learning or retention can be investigated.
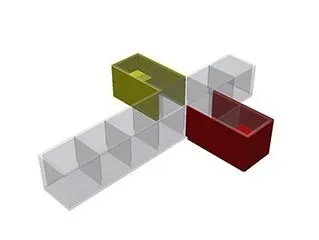
Cross maze
The aquatic cross maze is a multifunctional maze for zebrafish learning and memory testing, but also for social preference.
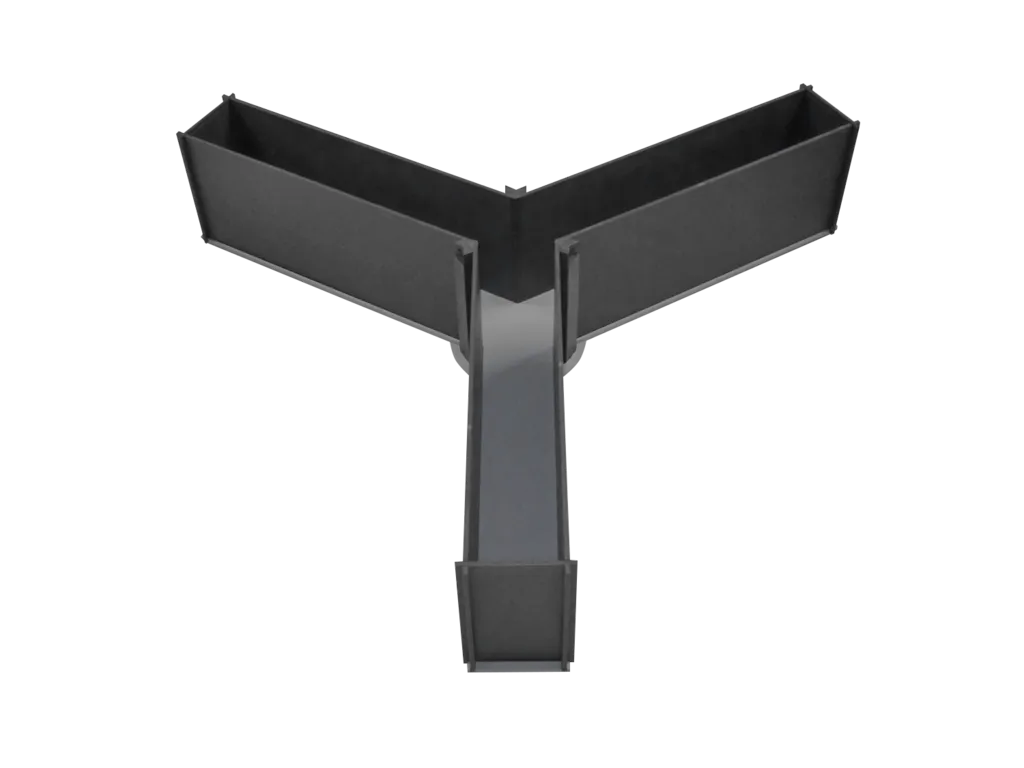

Y-maze
The Y-maze is a test to investigate spatial learning and memory. This maze is specifically designed for testing rodents.
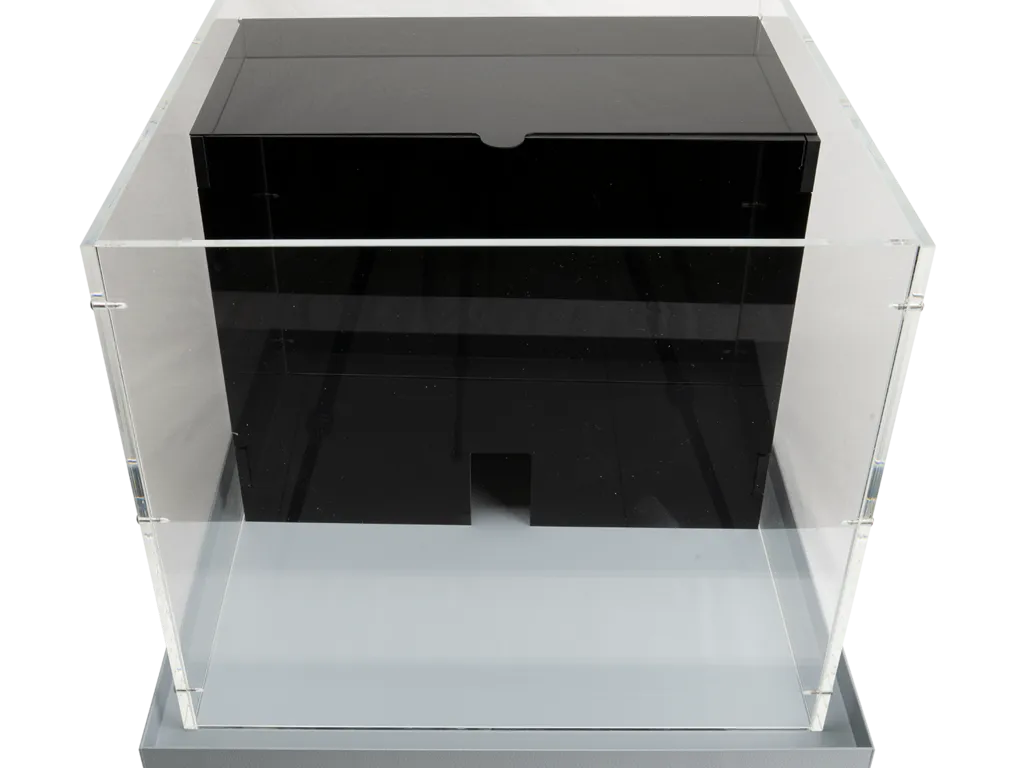

Light-dark box
The light-dark box is used to test the unconditioned anxiety response, based on a novel environment and light/open space.
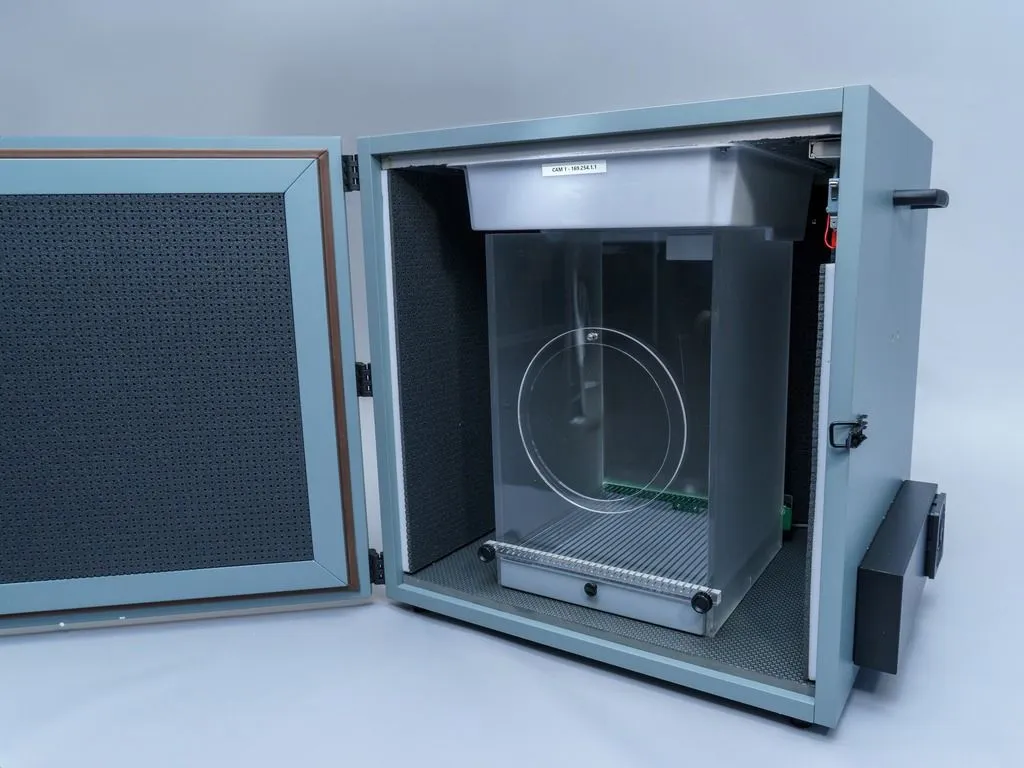
Fear conditioning
Fear conditioning and other learning tasks in rodents are typical in a wide range of neuropharmacological studies, amongst others.
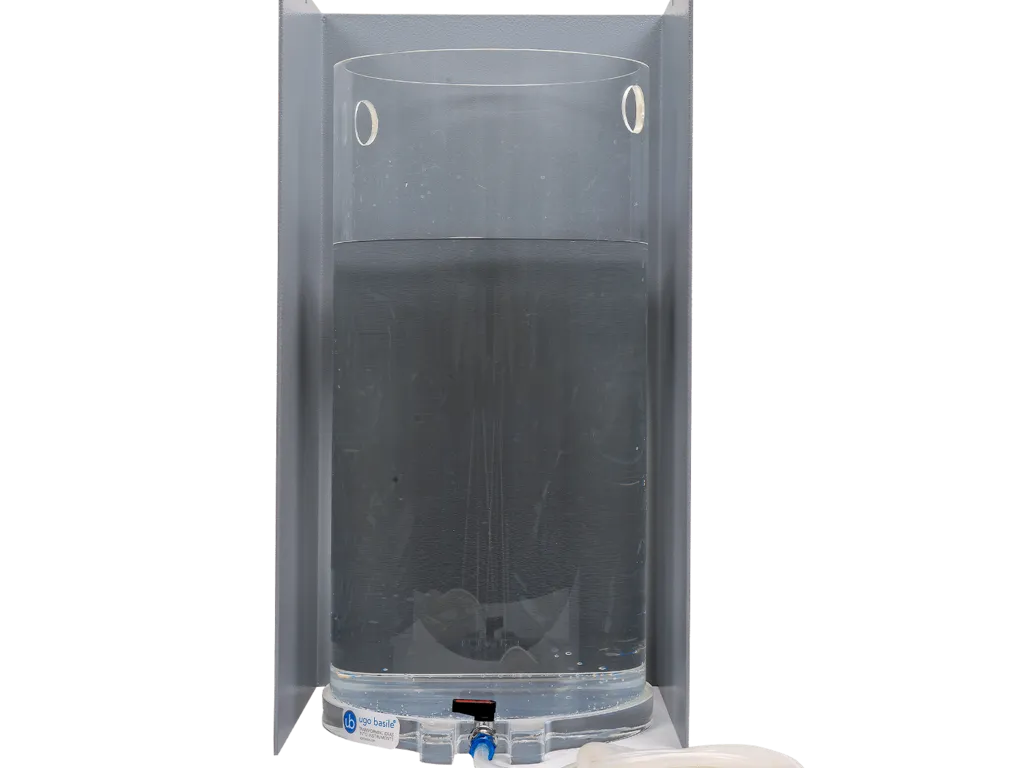

Forced swim test
The (Porsolt) forced swim test, also known as the behavioral despair test, is used to test for depression-like behavior in both mice and rats.
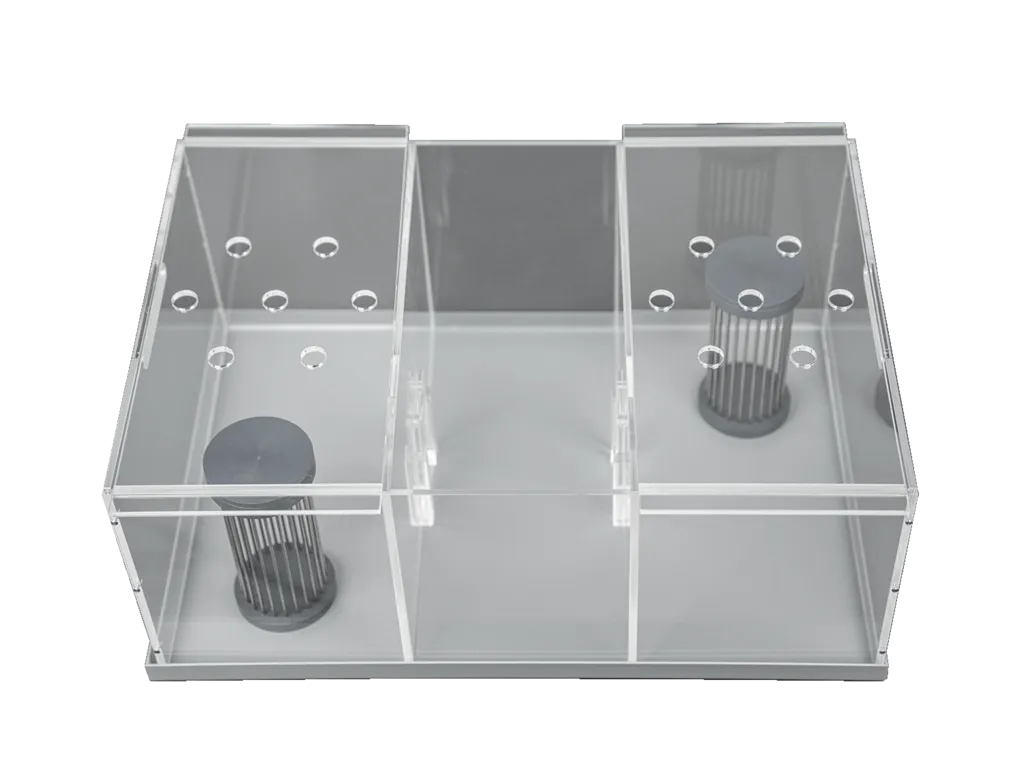

Sociability cage
Or three chamber test, is designed to test the social behavior or social memory of one individual towards others. Automatically detect the time spend near cage
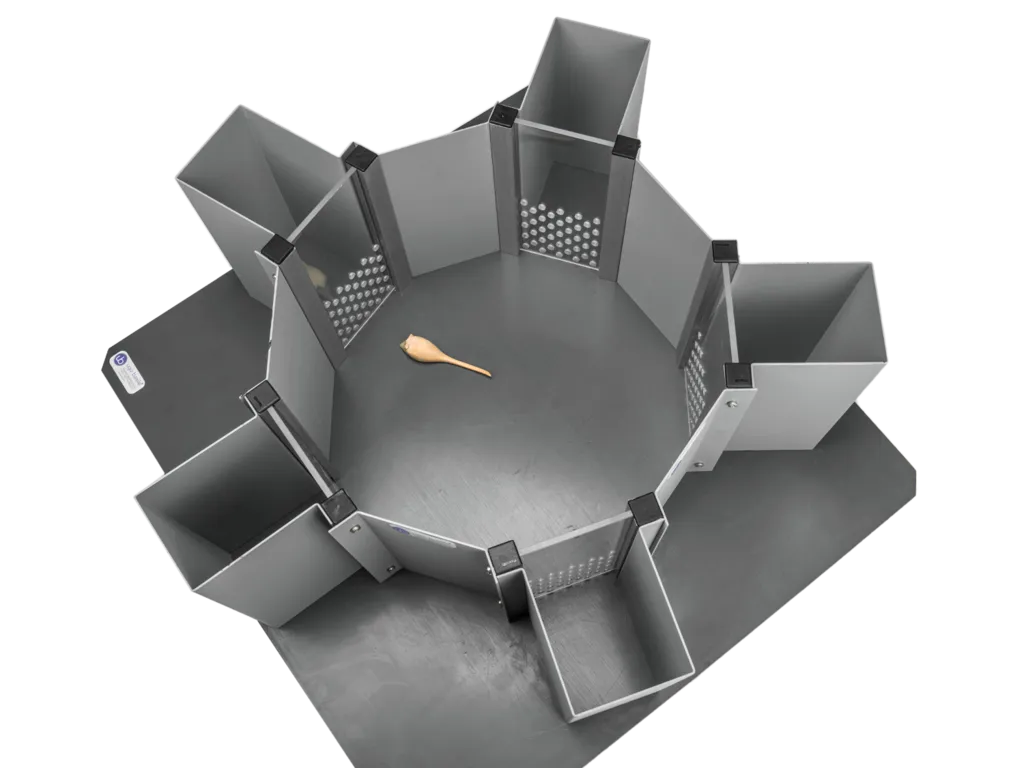

Agora maze
The Agora maze is a new sociability test, also known as the Sociobox method. The Agora maze diagnoses social recognition deficits.
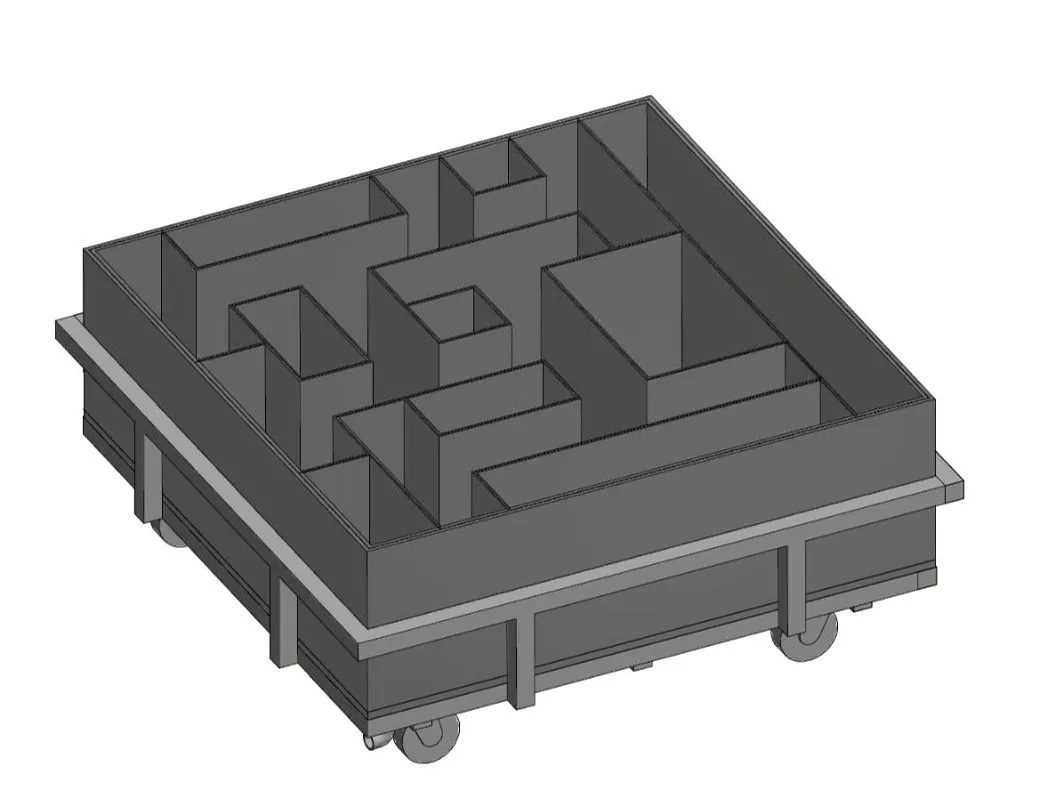
Cincinnati Maze
The Biel/Cincinnati Water Maze is used for studying egocentric navigation, learning, and memory. Often filled with water to motivate the animal to escape.
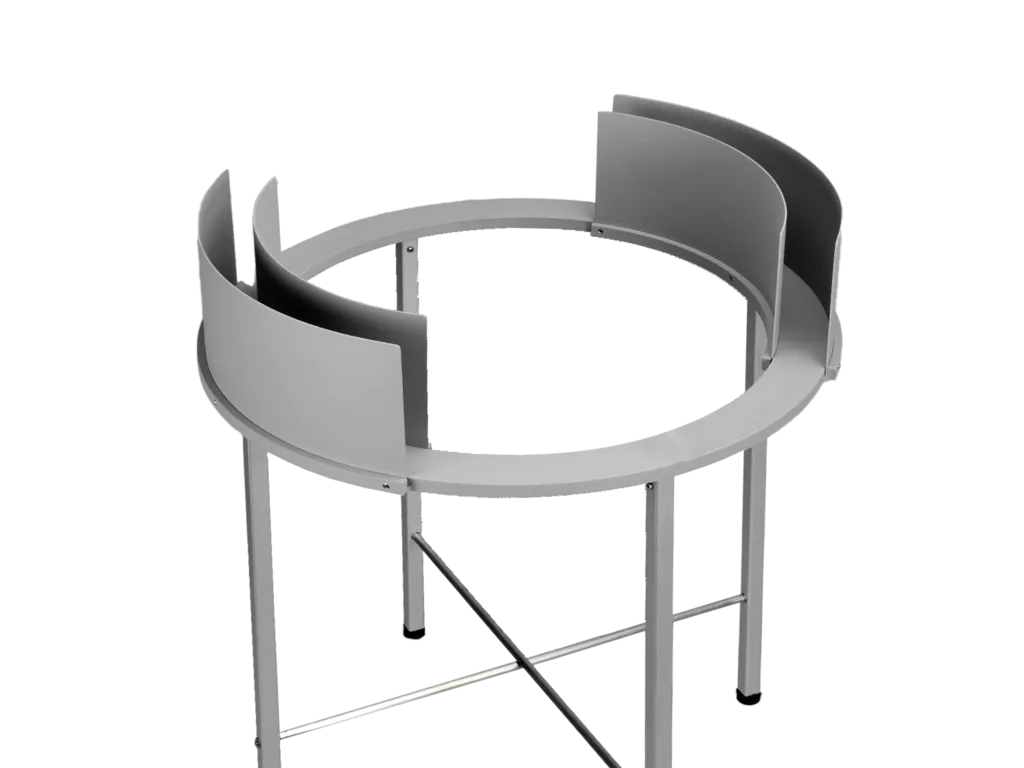

Zero maze
The elevated zero maze is very similar to the elevated plus maze, but lacks a center square. Gives an indication of anxiety versus exploration.
Learn more about mazes with EthoVision XT
There is a wide range of mazes available and described in literature for the behavioral assessment of animal models. For objective data collection, video tracking software is a must. We offer any type of maze, standard or custom, and always perfectly suited for video tracking with EthoVision XT.
Don't know where to start?
We're happy to help
Book a meeting for an online or onsite session.
Together, we can discuss your research requirements and come up with the best solution!