Galvanic skin response, heart rate variability and more behavior on the inside
When it comes to measuring our emotional responses to food items, medical treatment, or works of art, our behavior does not always paint the whole picture.
Posted by
Published on
Tue 15 May. 2012
Topics
| Consumer Behavior | Data Integration | Emotion Recognition | Emotions | Heart Rate | Measure Emotions | Methods And Techniques | Neuromarketing | Physiology | The Observer XT |

When it comes to measuring our emotional responses to food items, medical treatment, or works of art, our behavior does not always paint the whole picture. Sometimes it is difficult to put our emotional experience into words, for example, when looking at a painting in a museum. In other, more experimental situations, a test participant may be too young to verbally comment on the test situation or the participant is reluctant to show a behavioral response.
Galvanic skin response, heart rate variability and more behavior on the inside
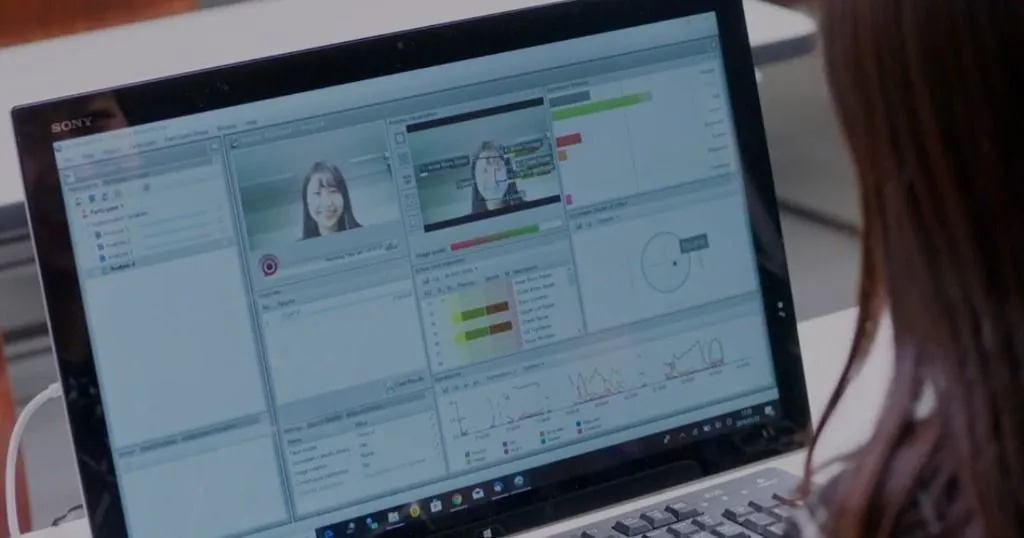
That is why behavioral researchers increasingly combine behavioral observations with psychophysiological measures, including heart rate and skin conductance. Skin conductance, or Galvanic Skin Response (GSR), measures the electrical conductance of the skin, which varies with sweat gland activity.
In behavioral research, GSR is used to gauge emotional arousal, indicating responses like stress, excitement, or boredom, as increased skin conductance reflects heightened physiological arousal, often linked to subconscious reactions.
Mapping museum experience
A good example of this is the “eMotion. Mapping museum experience” project of the University of Friedrichshaven in Germany [1].
The researchers measured the response of 500 visitors to different works of modern art in the museum of Sankt Gallen. They measured how long visitors looked at each work of art and, during the visit, they monitored physiological measures such as heart rate and skin conductance.
They found by combining the results of interviews, behavioral observations and the physiological measurements, that the physiological measures were significantly related to the aesthetic-emotional experience of an artwork. The researchers say that they could not have found this by only looking at the behavior of the visitors.
Consumer testing of new food products
Another example is consumer testing of new food products [2]. Researchers from Wageningen University and Research Center, The Netherlands state that consumer acceptance of new food products are not only affected by conscious processes but may also be based on unconscious processes, which may be measured by implicit physiological and behavioral measures.
In their study, they measured facial expressions, heart rate, skin conductance, and finger temperature in response to the presentation of liked and disliked food items. They found that the physiological measures provide detailed information on food preferences in relation to specific food properties that may not have been provided by behavioral measures only.
Data integration software
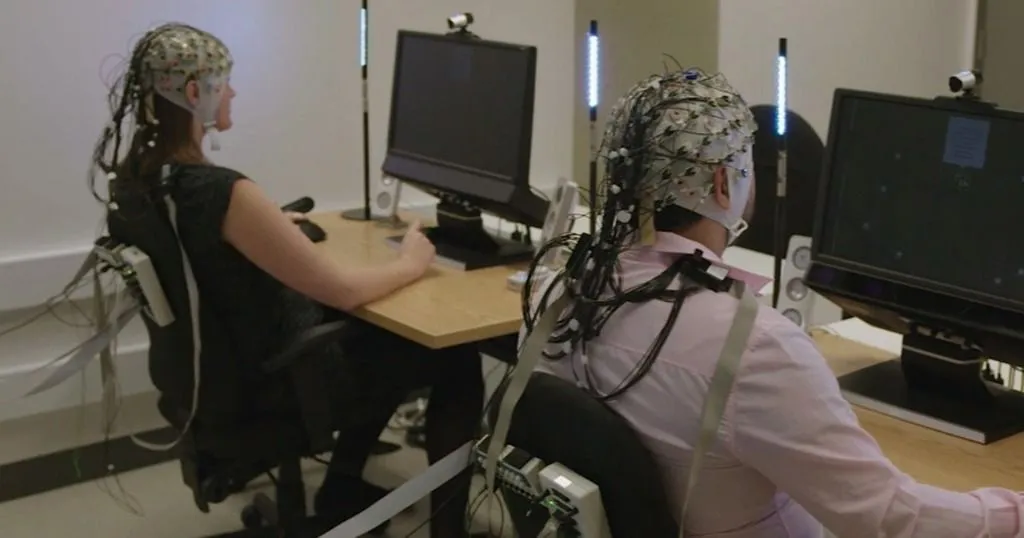
Emotional responses of humans to their social and physical environment are the subject of many psychological and behavioral studies. The Observer XT is a very useful tool to integrate behavioral and physiological data. As such, it can be used in large variety of research areas, ranging from consumer sciences to the study of the perception of art.
Another useful tool for multimodal research is NoldusHub. NoldusHub captures multiple behavioral and physiological signals, helping you understand motivations, emotions, and decisions. It streamlines the setup, connecting all your devices and synchronizing data from webcams, eye-trackers, and sensors.

References
[1] http://www.mapping-museum-experience.com/en
[2] Wijk, R. de; Kooijman, V.; Verhoeven, R.; Holthuyzen, N.; Graaf, C. de. (article in press) Autonomic nervous system responses on and facial expressions to the sight, smell, and taste of liked and disliked foods. Food Quality and Preference. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.foodqual.2012.04.015
Related Posts
SUKIPANI: The magic word for making a smile
What is biometric research?
